Marble Fox
45-68 cm
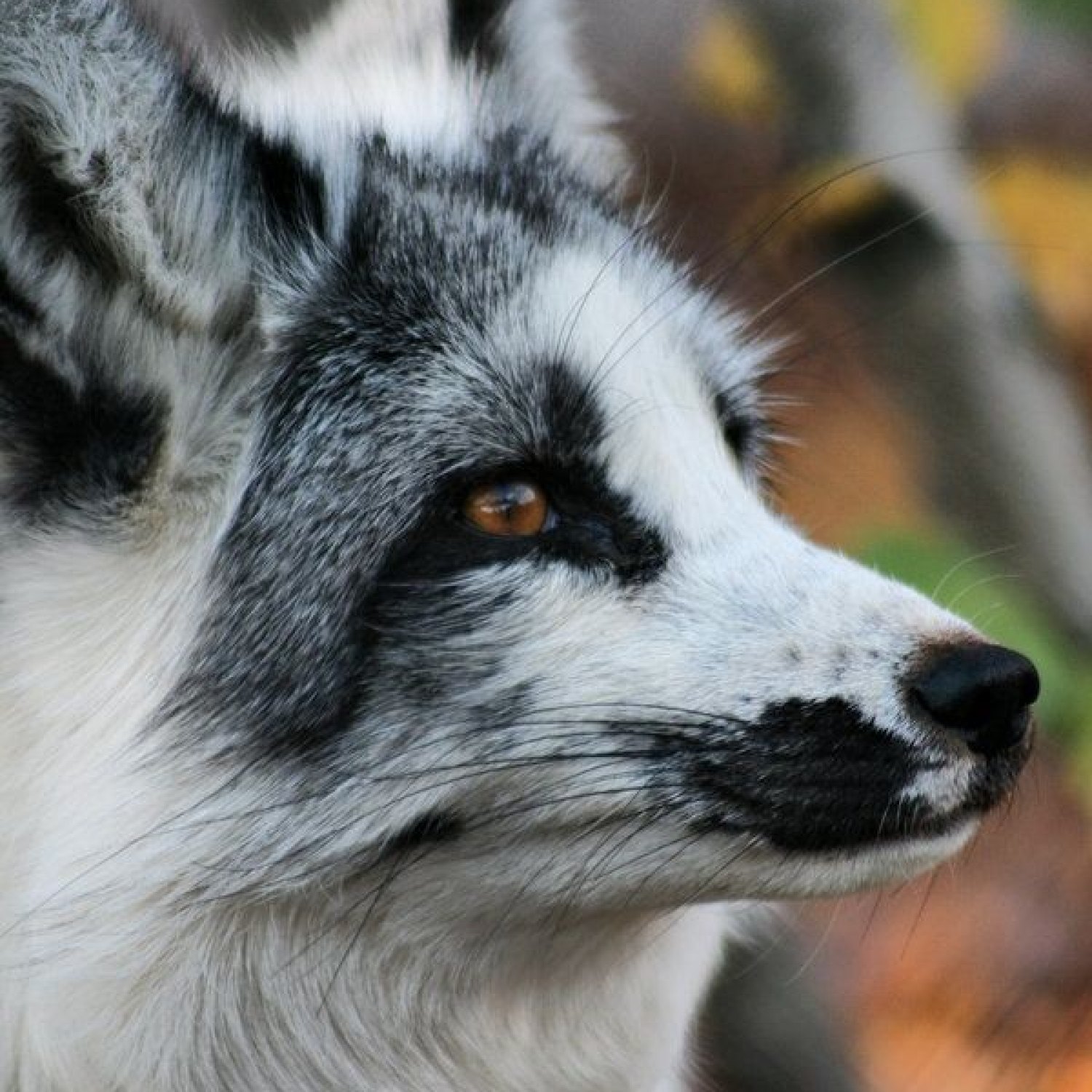
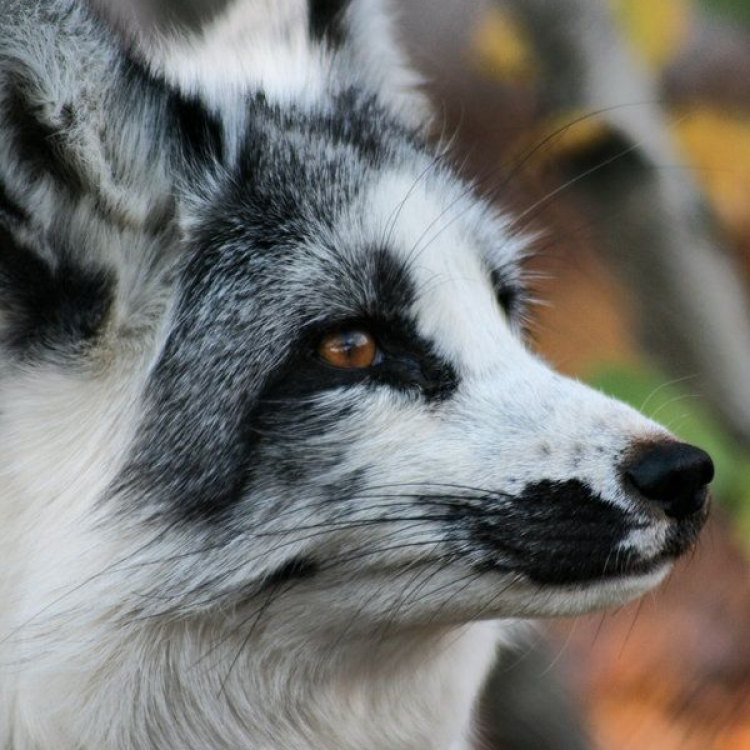
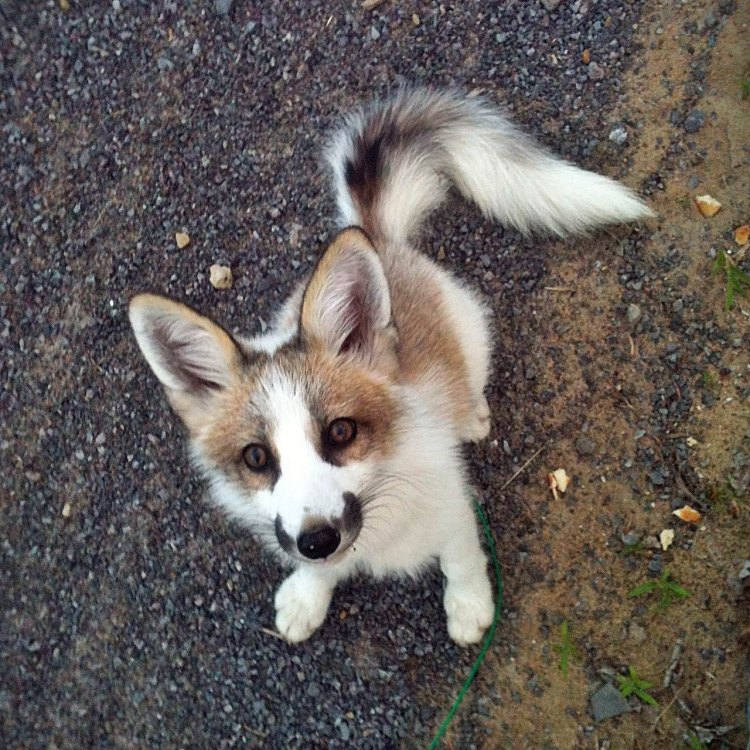
The Marble Fox, known for its stunning white and black coat, can be found in Northwestern Canada. Belonging to the Canidae family, these small and slender creatures can grow up to 45-68 cm long. Their unique coloration helps them blend in with their surroundings, making them an elusive sight in the wild. #MarbleFox #Wildlife #Canada
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Marble Fox
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Arctic tundra, boreal forests
The Enchanting Marble Fox: A Unique and Adaptable Canine
Step into the world of the Arctic tundra and boreal forests, and you may be lucky enough to catch a glimpse of a stunning creature known as the Marble Fox. While it may sound like an animal from a fairy tale, the Marble Fox is a real and fascinating animal found in the wilds of North America. Its scientific name is Vulpes vulpes, but it is more commonly known as the Marble Fox. Let's take a closer look at this enchanting creature and discover what makes it such a unique and adaptable member of the animal kingdom Marble Fox.A Rare and Adorned Species
The Marble Fox belongs to the Kingdom Animalia and the Phylum Chordata, just like millions of other animal species. However, what makes this animal truly stand out is its scientific name, which translates to "fox fox." This unique name derives from the fox's sleek and slender appearance, which is similar to its cousin, the red fox. Yet, while the red fox's coat is usually a rusty red color, the Marble Fox's coat is a dazzling white.In fact, the Marble Fox's coat is its most distinct feature and what gives it its name. This animal has a beautiful white base coat, adorned with striking black, gray, and brown markings. These markings vary from one fox to another, making each individual look like it has been delicately painted with marble. The Marble Fox's fur is not only visually stunning, but it also serves an essential purpose. In its natural habitat, the white coat helps the fox blend into the snowy landscape, making it a skilled hunter Millipede.
An Adaptable Habitat
The Marble Fox is a member of the Carnivora order, and with its sharp teeth and hunting skills, it certainly lives up to its name. This species is a carnivore, which means that it feeds solely on meat. Its primary sources of food include small mammals such as rodents, birds, and insects. However, the Marble Fox is known for being opportunistic, and it will also scavenge for food when necessary.Unlike many other species, the Marble Fox is not tied to one specific habitat. It can be found in both the Arctic tundra and boreal forests, making it an incredibly adaptable animal. The Arctic tundra is known for its harsh, frozen conditions, while the boreal forests are characterized by dense and coniferous trees. Despite these vastly different environments, the Marble Fox has successfully adapted to both, proving its ability to thrive in a variety of habitats.
A Home in Canada
While the Marble Fox's geographical distribution ranges across North America, it is primarily found in Canada. Its country of origin is also Canada, specifically in the northwestern region. The northwestern part of Canada is known for its remote and rugged terrain, with vast stretches of tundra and forests. This makes it an ideal location for the Marble Fox to make its home. The Marble Fox is often found in these parts, where it can roam freely and hunt for food.A Small and Slender Fox
In terms of physical appearance, the Marble Fox is a small and slender animal. On average, it measures between 45-68 cm in length and stands at a height of 25-30 cm. Its small stature allows it to move quickly and easily through the snow and dense forests. The Marble Fox also has a bushy tail, which helps to keep it warm in the frigid temperatures of its habitat.The Threat of Climate Change
Unfortunately, like many other animals, the Marble Fox is facing the threat of climate change. As global temperatures rise, the Arctic tundra and boreal forests are changing, making it challenging for the Marble Fox to adapt. The changing climate is causing a decrease in the availability of a vital prey species, the snowshoe hare. This could have a significant impact on the Marble Fox population. Fortunately, conservation efforts are in place to educate the public on the importance of protecting the Arctic tundra and boreal forests. By reducing our carbon footprint, we can help to preserve the natural habitat of the Marble Fox and other animals that call it home.The Magic of the Marble Fox
In conclusion, the Marble Fox is a beautiful and remarkable animal that has captured the hearts of many. Its striking coat, adaptability, and unique abilities make it a fascinating member of the animal kingdom. Yet, despite its enchanting appearance, the Marble Fox is also a reminder of the impact of climate change on our planet and the importance of preserving our natural habitats. Let us cherish and admire the magic of the Marble Fox and strive to protect its home for generations to come.

Marble Fox
Animal Details Marble Fox - Scientific Name: Vulpes vulpes
- Category: Animals M
- Scientific Name: Vulpes vulpes
- Common Name: Marble Fox
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Carnivora
- Family: Canidae
- Habitat: Arctic tundra, boreal forests
- Feeding Method: Carnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: North America
- Country of Origin: Canada
- Location: Northwestern Canada
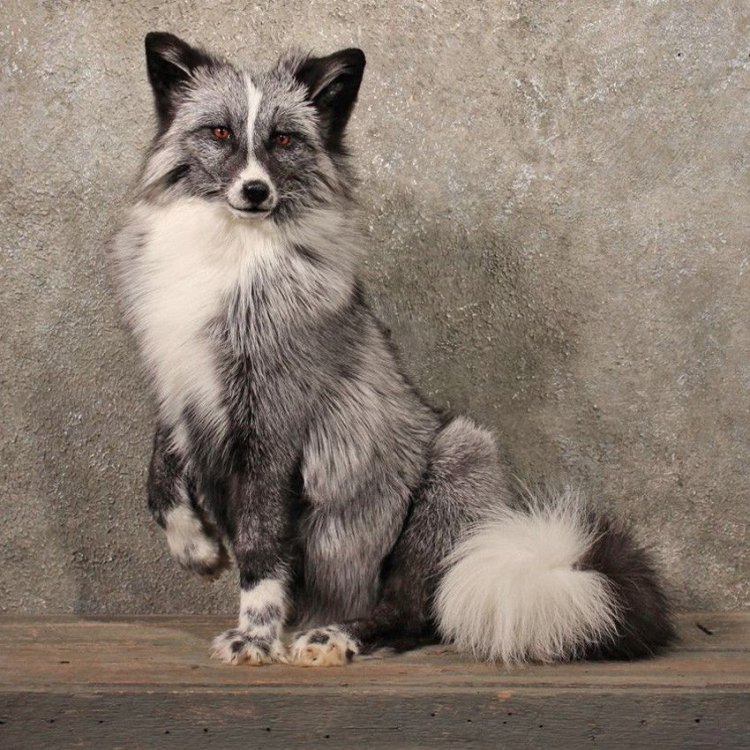
- Animal Coloration: White with black, gray, and brown markings
- Body Shape: Small and slender
- Length: 45-68 cm

Marble Fox
- Adult Size: Medium-sized
- Average Lifespan: 3-4 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Breeding occurs in winter
- Sound or Call: Barking and howling
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Solitary or live in small family groups
- Behavior: Nocturnal and crepuscular
- Threats: Habitat loss, climate change, hunting
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Impact on Ecosystem: Predator in the ecosystem
- Human Use: Fur trade
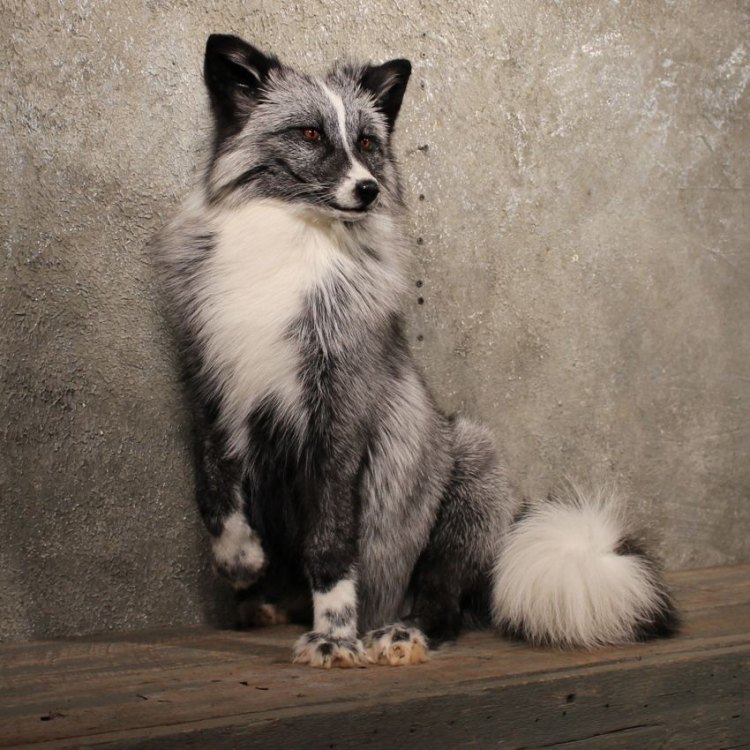
- Distinctive Features: Long bushy tail, black eye patches
- Interesting Facts: Marble foxes are color variants of the red fox
- Predator: Wolves, humans

Vulpes vulpes
The Enigmatic Marble Fox: Masters of Survival
In the vast landscape of the arctic region, where the bitter cold wind and snow dominate the land, there roams a creature that captivates the hearts of many – the marble fox. Often mistaken as a mythical creature due to its beautiful and unique appearance, the marble fox is a true wonder of nature.Marble foxes, also known as Arctic foxes or white foxes, are a color variant of the more commonly known red fox. Their scientific name, Vulpes lagopus, translates to “hare-footed fox,” a tribute to their large and furry paws that help them navigate through the harsh Arctic terrain PeaceOfAnimals.Com. These majestic creatures are native to the Arctic tundra and taiga regions, found in Canada, Alaska, Russia, Northern Europe, and Greenland.
Adult sized marble foxes are considered medium-sized, with an average length of 22-25 inches and a weight of 6-12 pounds. They are smaller in size compared to their red fox counterparts, but what they lack in size, they make up for in their captivating beauty.
One of the most interesting facts about marble foxes is their distinctive coloration. While their cousins, the red foxes, may have different shades of brown, rust, and red in their fur, marble foxes are predominantly white with black markings on their backs, legs, and face. The black eye patches on their faces give them a fierce and mysterious appearance often seen in folklore and myths. These stunning creatures have thick, full fur, which helps them survive in the extreme cold temperatures of the Arctic.
Marble foxes have a relatively short lifespan of 3-4 years in the wild, with some individuals living up to 11 years in captivity. This may seem like a short time, but they have managed to survive and thrive in some of the harshest environments on earth Mule.
Reproduction in marble foxes is sexual, with breeding occurring in the winter months of January to March. This timing allows the babies, called kits, to be born in the warmer months, increasing their chances of survival. After a gestation period of about 50 days, the female gives birth to a litter of 5-8 kits, blind and helpless at birth. The dominant male and female in the group take on the role of caring for and protecting the kits until they are old enough to fend for themselves.
Marble foxes are solitary animals, but they can also live in small family groups consisting of a dominant male, a dominant female, and their young. They are often active at night and during the twilight hours, making them nocturnal and crepuscular animals. This behavior helps them avoid predators and scorching temperatures during the long summer days in the Arctic.
One of the most distinct features of the marble fox is their long, bushy tail. Their tail serves multiple purposes, from helping them balance while running and jumping on the snow, to serving as a warm blanket when they curl up to rest. Their long tail also plays a significant role in communication among members of the same species.
Marble foxes are excellent communicators, using various vocalizations to communicate with their family members. They can bark, growl, and howl, with their calls audible from far distances. Their communication skills also extend to their sense of smell, which is highly developed, allowing them to locate prey and potential mates from afar.
In the ecosystem, marble foxes play an essential role as predators. They mainly feed on small animals such as lemmings, voles, Arctic hares, and birds. Their sharp hunting skills and swift movements allow them to catch their prey, making them vital in regulating the population of these species.
However, like many other species, marble foxes face numerous threats to their survival. Habitat loss, due to human development and climate change, is one of the significant threats to these creatures. With melting sea ice due to rising temperatures, their habitat is gradually shrinking, reducing their available resources, such as food and shelter. Additionally, hunting for their luxurious fur, also known as the fur trade, poses a significant threat to their survival. Although hunting is regulated in many countries, illegal poaching still occurs, contributing to the decline in their population.
Despite these threats, the marble fox remains classified as “least concern” on the IUCN Red List, thanks to their ability to adapt and survive in harsh environments.
Humans have long been fascinated by the beauty and grace of the marble fox and have been using their fur for various purposes for centuries. Their thick, soft fur is highly sought after in the fur trade, used for fashion and decorative purposes. However, due to conservation efforts, the use of marble fox fur has reduced significantly, and alternatives such as faux fur are becoming more popular.
Marble foxes may have their fair share of predators, including wolves and humans, but it is their ability to adapt to their surroundings that has allowed them to thrive in the ever-changing Arctic landscape.
In conclusion, the marble fox is a remarkable creature that captures the imagination and hearts of many. With their unique and stunning appearance, and their remarkable survival skills, they have proven to be masters of survival in one of the harshest environments on earth. As we continue to learn more about them and work towards their conservation, we can only hope for their continued presence in the Arctic for generations to come.

The Enchanting Marble Fox: A Unique and Adaptable Canine
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.