Viperfish
Up to 30 cm
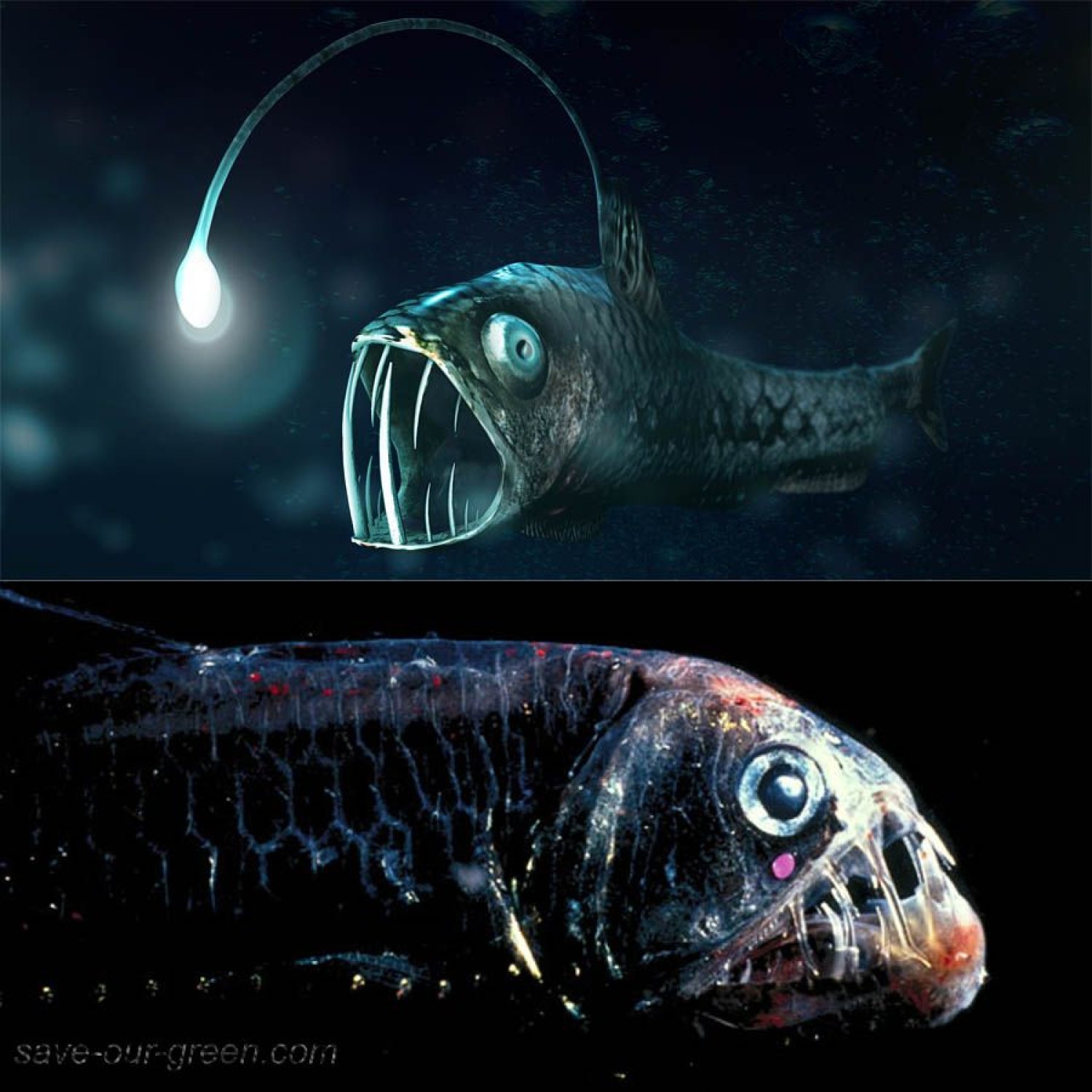
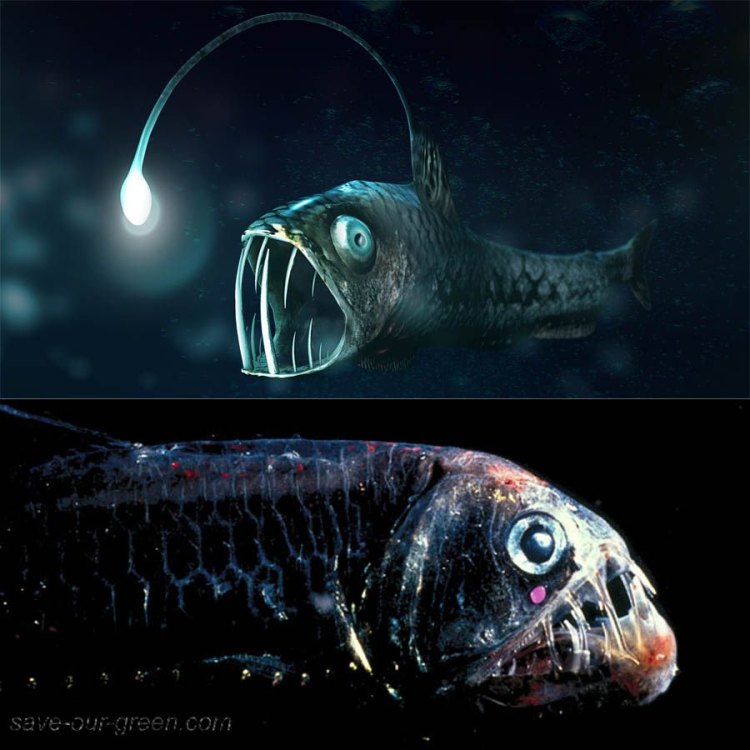
Viperfish, with a length of up to 30 cm, is an extraordinary deep-sea creature found in oceanic waters. This member of the Stomiidae family has an elongated and slender body, giving it a viper-like appearance. Their large, needle-like teeth make them apex predators in their habitat. Spot them in the deep, dark depths of the ocean if you dare! #Viperfish #DeepSeaCreatures #Stomiidae #OceanLife
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Viperfish
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Deep-sea
The Mysterious and Deadly Viperfish: Exploring the Depths of the Deep-Sea Kingdom
The deep-sea is a world of wonders, filled with creatures that seem to be from another planet. One of these creatures is the viperfish, also known as Chauliodus sloani. This mysterious and deadly fish belongs to the kingdom Animalia and the phylum Chordata, making it a distant relative of humans and other vertebrates.The viperfish is a member of the Actinopterygii class, which is home to over 95% of all fish species Viperfish. Its order, Stomiiformes, includes a variety of deep-sea fish that possess bioluminescent organs, allowing them to produce light in the dark depths of the ocean. The viperfish, with its unique characteristics and predatory instincts, has found its place in the world of deep-sea creatures.
Appearance and Distribution
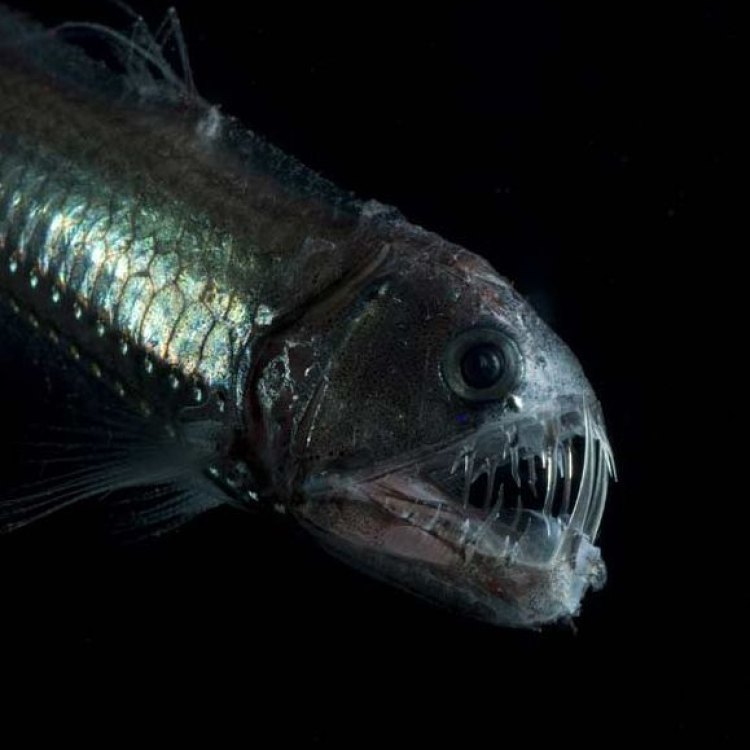
The viperfish is a small but terrifying fish, growing up to 30 cm in length. Its body is elongated and slender, perfectly adapted for life in the deep-sea. Its most distinctive feature is its long and sharp fang-like teeth, giving it the appearance of a deadly serpent, hence its name "viperfish."The viperfish is widely distributed in the world's oceans, with sightings recorded off the coast of North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia. These fish inhabit the mesopelagic zone, which is the middle layer of the ocean, between the epipelagic (surface) and bathypelagic (deep) zones. They are found at depths of up to 900 meters, with some species being able to go even deeper.
Habitat and Adaptations
The viperfish lives in a world of complete darkness, where the pressure is immense, and the temperature is close to freezing Vine Snake. These conditions would be unbearable for most creatures, but the viperfish has evolved to thrive in this harsh environment. Its body is covered with dark pigmentation, allowing it to blend in with its surroundings, making it nearly invisible to predators and prey alike.One of the most fascinating adaptations of the viperfish is its bioluminescent organ, located on its chin. This organ contains luminous bacteria that help the fish produce light, attracting prey and potential mates. The viperfish also has long modified dorsal and anal fin rays, commonly known as "illicia," which are used to lure prey closer to its mouth.
Feeding and Predatory Methods
The viperfish is a ferocious carnivore, feeding on smaller fish, squid, and crustaceans. Its sharp fang-like teeth are not used for chewing, but rather for grasping and impaling its prey. The viperfish's jaw is hinged, allowing it to open its mouth wide and swallow prey larger than itself.Due to the limited amount of food available in its deep-sea habitat, the viperfish has developed an efficient feeding strategy. It often remains still, conserving energy, and uses its bioluminescent organ to attract prey. Once its prey is in range, the viperfish attacks with astonishing speed, using its sharp teeth to secure its meal.
A Role in the Ecosystem
The viperfish may be a top predator but is also an essential member of the deep-sea ecosystem. Its feeding habits help to control the population of smaller fish and maintain a healthy balance in its habitat. The viperfish also serves as a food source for larger deep-sea creatures, contributing to the flow of energy in the ocean's food chain.This fish is also known for its role in scientific research. Its unique adaptations and ability to survive in extreme environments have caught the interest of scientists, who continue to study and learn from the viperfish.
Conservation Status and Threats
As a deep-sea species, the viperfish is not directly threatened by human activities. However, it is still affected by the impacts of climate change, such as ocean acidification and rising water temperatures. These changes can disrupt the entire marine ecosystem, potentially affecting the viperfish's food sources and survival.Additionally, the viperfish is often caught as bycatch in commercial fishing operations. While it is not a targeted species, being unintentionally caught and discarded can still have a significant impact on its population. Therefore, sustainable fishing practices and reducing plastic pollution in the ocean are crucial in protecting the viperfish and other deep-sea creatures.
The Fascinating World of the Viperfish
The viperfish may seem like a creature from a horror movie, but in reality, it is a fascinating and vital species in the deep sea. Its unique adaptations, bioluminescent abilities, and predatory instincts make it a fearsome and impressive creature. As we continue to explore and learn about the deep-sea, we may uncover even more secrets and mysteries about this elusive fish.However, with the ever-increasing threats to our oceans, the viperfish's future remains uncertain. It's up to us to take action and protect these magnificent creatures and the delicate ecosystems they inhabit. By reducing our impact on the environment and promoting sustainable practices, we can ensure that the viperfish and other deep-sea creatures continue to thrive for generations to come.

Viperfish
Animal Details Viperfish - Scientific Name: Chauliodus sloani
- Category: Animals V
- Scientific Name: Chauliodus sloani
- Common Name: Viperfish
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Actinopterygii
- Order: Stomiiformes
- Family: Stomiidae
- Habitat: Deep-sea
- Feeding Method: Carnivore
- Geographical Distribution: Worldwide
- Country of Origin: N/A
- Location: Oceanic waters
- Animal Coloration: Dark
- Body Shape: Elongated and slender
- Length: Up to 30 cm

Viperfish
- Adult Size: Up to 30 cm
- Average Lifespan: Up to 20 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Unknown
- Sound or Call: Unknown
- Migration Pattern: Unknown
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: Aggressive ambush predator
- Threats: Overfishing, habitat destruction
- Conservation Status: Not evaluated
- Impact on Ecosystem: Maintains balance in deep-sea food chain
- Human Use: Rarely targeted for fishing
- Distinctive Features: Large mouth, long fang-like teeth, bioluminescent lure
- Interesting Facts: Viperfish have one of the fastest strike speeds recorded for a fish
- Predator: Unknown

Chauliodus sloani
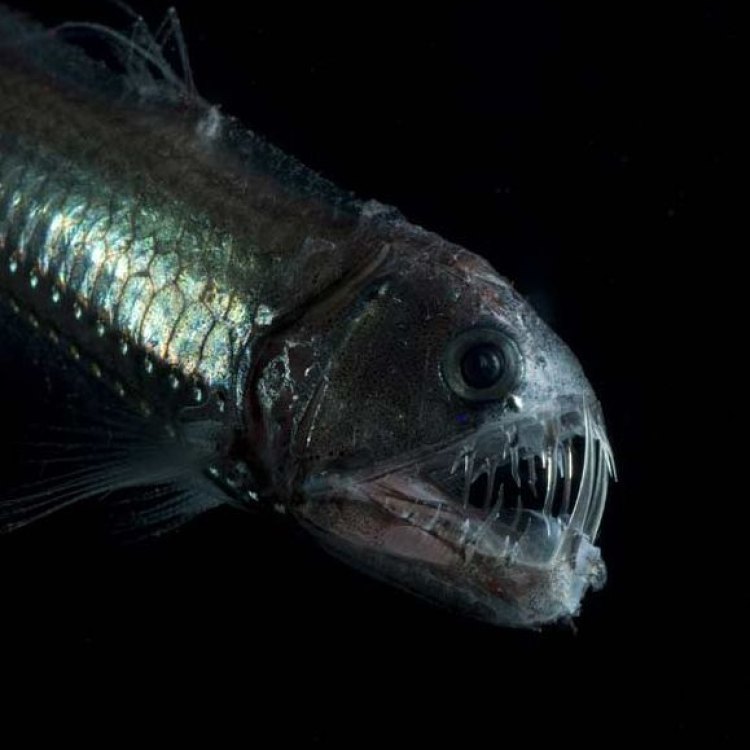
The Fearsome Viperfish: A Hidden and Mysterious Predator of the Deep Sea
Deep in the dark depths of the ocean, a creature lurks in the shadows, waiting patiently for its unsuspecting prey. With razor-sharp fang-like teeth and a bioluminescent lure, the viperfish is truly a unique and fearsome predator. In this article, we will take a closer look at this mysterious creature and discover its interesting features, behavior, and impact on the ecosystem.Native to the world's oceans, the viperfish (genus Chauliodus) is a small but deadly creature that belongs to the family Stomiidae, also known as the dragonfish family PeaceOfAnimals.Com. They are found in all the major oceans, often dwelling in depths of up to 5,000 feet. The name 'viperfish' is derived from its large mouth and long fang-like teeth, which resemble that of a viper snake.
Size and Lifespan
The average size of an adult viperfish is around 20 to 30 cm, although some individuals can grow up to 60 cm. They have a slender, eel-like body with a narrow head and large eyes adapted for hunting in low light conditions. As deep-sea creatures, they have a longer lifespan compared to other fish, with an average life expectancy of up to 20 years.
Reproduction and Behavior
Not much is known about the reproductive behavior of the viperfish due to their elusive nature. However, it is known that they reproduce sexually, with males fertilizing the eggs externally. Some species of viperfish, such as the Pacific viperfish, are known to undergo vertical migration, swimming to shallower waters at night to mate and returning to the depths during the day.
As solitary creatures, viperfish are not known to form social groups Venus Flytrap. They are aggressive ambush predators, patiently waiting for their prey to come within striking distance. They have specialized bioluminescent organs located along their sides, which help them in attracting prey with their glowing lure. Once the prey is lured in, the viperfish strikes at lightning speed, using its sharp teeth to impale and catch its victim. They are known to have one of the fastest strike speeds recorded for a fish, making them incredibly efficient hunters.
Threats and Conservation Status
Humans are the biggest threat to the viperfish, as their deep-sea habitats are not immune to the negative impacts of human activities such as overfishing and habitat destruction. While they are not specifically targeted for fishing, viperfish often get caught in commercial fishing nets as bycatch, which can significantly impact their population. Their habitat is also at risk due to deep-sea mining activities and pollution, further endangering their survival.
Despite these threats, the viperfish is not yet evaluated for conservation status by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This is due to the lack of information on their population status and behavior. However, as top predators in the deep-sea food chain, the decline of the viperfish population could have a cascading effect on the entire ecosystem.
Impact on the Ecosystem
As an apex predator, the viperfish plays a crucial role in maintaining balance in the deep-sea food chain. They keep prey populations in check, preventing them from becoming overpopulated and competing for resources. This, in turn, helps to maintain the health and stability of the entire ecosystem. The bioluminescent organs of the viperfish also serve as a vital source of light in the deep, dark waters, making it easier for other organisms to navigate and find their prey.
Human Use and Interesting Facts
Despite their fearsome appearance, viperfish are not commonly targeted for fishing due to their small size and deep-sea habitat. They are often caught as bycatch and rarely consumed by humans. However, their unique bioluminescent lure has made them a popular subject of interest for research and aquariums, where they can be found in specialized deep-sea exhibits.
One of the most interesting facts about the viperfish is its incredible strike speed. In 2012, a study conducted by researchers at the University of Victoria in Canada found that some species of viperfish can strike at their prey at speeds of up to 95 kilometers per hour, making them one of the fastest animals in the ocean.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the viperfish is a highly elusive and fascinating creature that roams the depths of our oceans. With its distinctive features, aggressive behavior, and impact on the ecosystem, it is clear that the viperfish plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of the deep-sea food chain. It is vital for us to understand and protect these creatures and their habitats, as they are a vital part of our world's oceans. Let us continue to discover and appreciate the wonders of the deep sea, and ensure that these mysterious creatures are around for generations to come.

The Mysterious and Deadly Viperfish: Exploring the Depths of the Deep-Sea Kingdom
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.