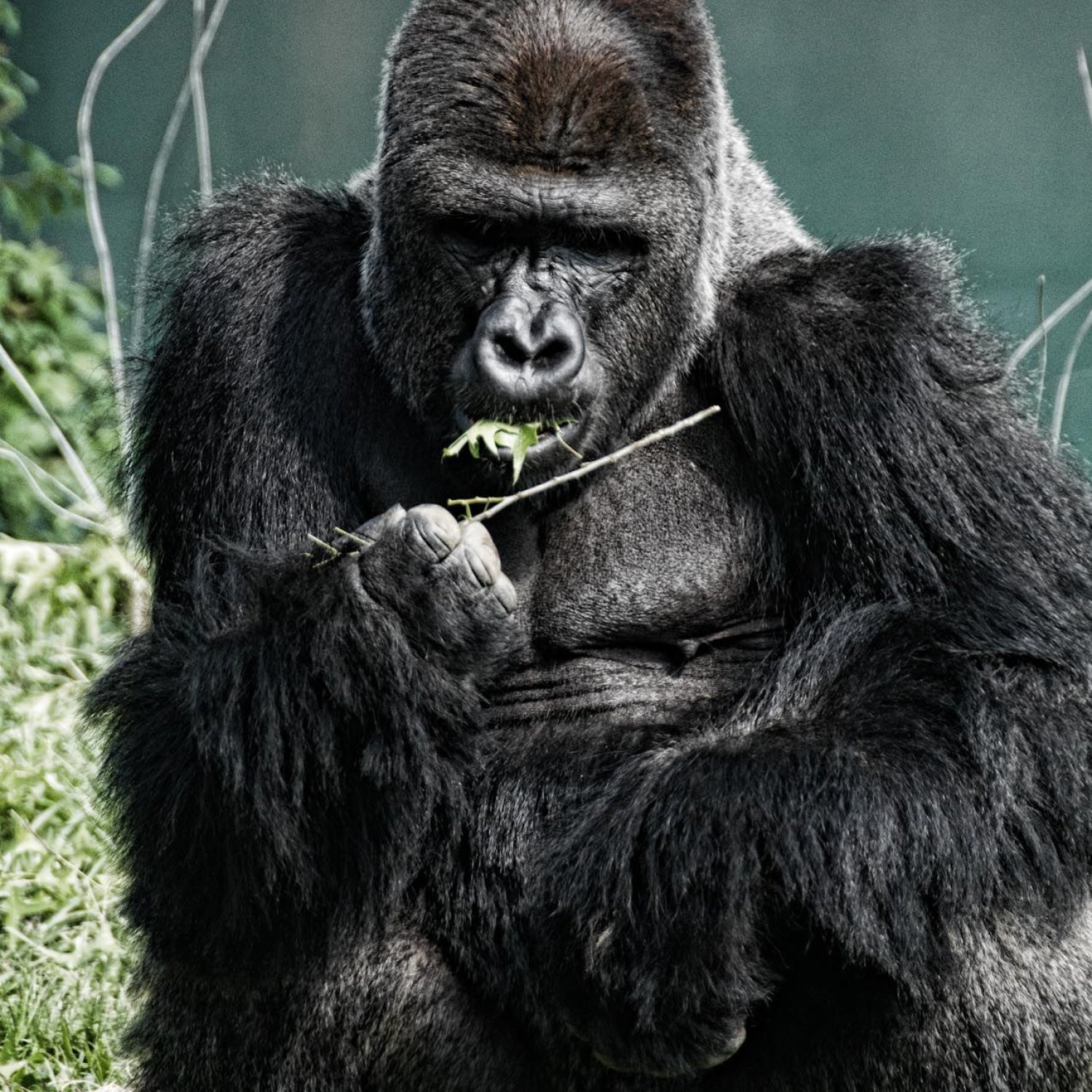
Eastern Gorilla
1.5 to 1.8 meters (males), 1.4 to 1.6 meters (females)
Did you know that the Eastern Gorilla is one of the largest primate species? Males can reach up to 1.8 meters in length while females average around 1.6 meters. They are found in the Virunga Mountains and Bwindi Impenetrable National Park, making it a popular destination for wildlife enthusiasts. Part of the Hominidae family, these majestic creatures have a large and bulky body shape, making them the king of the jungle.
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Eastern Gorilla
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Tropical rainforests
The Magnificent Eastern Gorilla: Exploring the Kingdom of the Largest Living Primate Species
In the lush tropical rainforests of eastern and central Africa resides a gentle giant of the animal kingdom, the Eastern Gorilla. With its scientific name, Gorilla beringei, this magnificent creature is the largest living primate species and holds a special place in the hearts of many people who are fascinated by its impressive size and gentle nature.The Eastern Gorilla, also known as the Mountain Gorilla, is a member of the Animalia kingdom, belonging to the phylum Chordata and class Mammalia. As primates, they are closely related to humans, sharing 98% of their DNA with us Eastern Gorilla. This connection to our own species adds to the intrigue and interest in getting to know these magnificent creatures.
A Habitat Fit for Kings of the Jungle
Eastern Gorillas are found in tropical rainforests, in countries such as the Democratic Republic of Congo, Uganda, and Rwanda. They reside mainly in two locations: the Virunga Mountains and the Bwindi Impenetrable National Park. Both of these places offer the perfect habitat for these gentle giants to thrive and flourish.The Virunga Mountains, situated along the borders of the Democratic Republic of Congo, Rwanda, and Uganda, are a chain of volcanoes that provide an ideal location for the Eastern Gorillas. With an elevation of over 4,000 meters, the mountain range creates a cool and humid climate, perfect for these rainforest dwelling creatures.
Similarly, the Bwindi Impenetrable National Park, located in southwestern Uganda, is a designated UNESCO World Heritage Site and home to over half of the world's remaining Mountain Gorilla population. This park provides a diverse habitat for the Eastern Gorillas, with its thick forest cover, steep slopes, and a variety of vegetation.
Both of these locations offer a peaceful and secluded haven for the Eastern Gorillas, allowing them to go about their daily activities without much disturbance Egyptian Mau.
Dining with Herbivores
While they may be known as the kings of the jungle, the Eastern Gorillas are not carnivorous predators like their lion or tiger counterparts. In fact, they are herbivores, with their diet consisting mostly of leaves, shoots, and stems of various plants. They also occasionally feed on fruit and bamboo when available.Their herbivorous diet contributes to their large size and bulky bodies, as they need a substantial amount of energy to sustain their massive frames. They are also equipped with powerful jaws and teeth to help them grind the tough vegetation they consume.
A Majestic Appearance
The Eastern Gorilla is a sight to behold with its massive size and striking black coloration, making it stand out against the backdrop of the lush green rainforests. The males, also known as silverbacks, can grow up to 1.8 meters in height and weigh between 140 to 200 kilograms, while females are slightly smaller, reaching heights of 1.6 meters and weighing between 60 to 100 kilograms.Their bodies are covered with long and coarse black fur, protecting them from the humid and cool climate of their habitat. They also have a pronounced ridge on their forehead, giving them a distinct appearance.
Family Ties and Hierarchy
Eastern Gorillas live in close-knit groups known as troops, led by the dominant male, the silverback. These troops can consist of anywhere between 2 to 30 individuals, with a typical group including one or two silverbacks, several adult females, and their young offspring.Within these troops, there is a well-established hierarchy, with the silverback being the leader and protector of the group. He makes all the important decisions, such as where to rest and feed, and ensures the safety of his family. The rest of the group follows his lead, with the females and young ones being submissive to his authority.
The Importance of Family Bonds
One of the most endearing qualities of the Eastern Gorillas is their strong family bonds. Within the group, there is a strong sense of loyalty and cooperation, with members looking out for each other's well-being. They communicate with each other through various vocalizations and body gestures, further strengthening their social bonds.The females are responsible for taking care of the young ones, with their close relationship with the silverback also ensuring the safety and protection of their offspring. This close-knit family dynamic is crucial for the survival of the Eastern Gorillas, as they rely on each other for protection and support.
Threats and Conservation Efforts
While the Eastern Gorilla may seem like a powerful and resilient creature, it is sadly classified as critically endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This designation is due to various threats that these magnificent animals face in the wild, including habitat loss, poaching, and disease.The destruction of their natural habitat through deforestation and human encroachment has heavily impacted the Eastern Gorilla population. Poaching for their body parts and bushmeat has also had a devastating effect on their numbers. Additionally, the spread of diseases such as Ebola, which affects both gorillas and humans, poses a significant threat to their survival.
However, there is hope for the Eastern Gorillas, thanks to conservation efforts by various organizations and governments. The Bwindi Impenetrable National Park and the Virunga Mountains have been declared protected areas, with strict regulations in place to prevent further habitat destruction and poaching.
Organizations such as the Dian Fossey Gorilla Fund and the International Gorilla Conservation Programme also work tirelessly to monitor and protect these animals, as well as conduct research to better understand their behaviors and needs.
A Symbol of Wildlife Conservation
The Eastern Gorilla's status as a critically endangered species serves as a reminder of the urgent need for wildlife conservation. These gentle giants are not just majestic creatures to admire, but they play a vital role in maintaining the balance of their ecosystem. Protecting them is crucial for the overall health of the rainforest and its inhabitants.Moreover, the efforts to conserve the Eastern Gorillas serve as a beacon of hope for other endangered species. With the right dedication and resources, we can make a positive impact on these animals and help them thrive for generations to come.
An Unforgettable Encounter
For those fortunate enough to have an encounter with the Eastern Gorillas in their natural habitat, it is a truly unforgettable experience. To be in the presence of these peaceful creatures, observing them go about their daily routines, is an awe-inspiring and humbling experience.Through responsible and ethical tourism, it is possible to embark on a gorilla trek and witness these magnificent animals in their natural environment. However, it is essential to ensure that these encounters do not disturb or harm the gorillas in any way, and that tourism is done sustainably and with the utmost respect for their wellbeing.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the Eastern Gorilla is a remarkable and awe-inspiring animal, with its sheer size, gentle nature, and strong family bonds. Despite facing numerous threats, efforts to protect and conserve these animals offer hope for their survival in the wild.It is our responsibility as fellow inhabitants of this planet to do our part in preserving the Eastern Gorilla and other endangered species. By raising awareness and supporting conservation efforts, we can ensure that the kings of the jungle continue to reign over their tropical rainforest kingdom for generations to come.
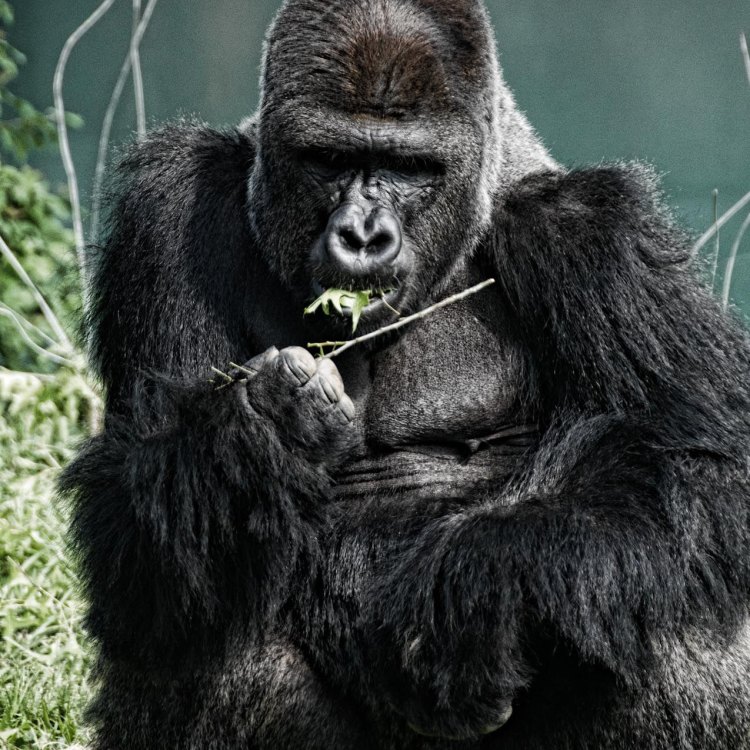

Eastern Gorilla
Animal Details Eastern Gorilla - Scientific Name: Gorilla beringei
- Category: Animals E
- Scientific Name: Gorilla beringei
- Common Name: Eastern Gorilla
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Primates
- Family: Hominidae
- Habitat: Tropical rainforests
- Feeding Method: Herbivore
- Geographical Distribution: Eastern and Central Africa
- Country of Origin: Democratic Republic of Congo, Uganda, Rwanda
- Location: Virunga Mountains, Bwindi Impenetrable National Park
- Animal Coloration: Black
- Body Shape: Large and bulky
- Length: 1.5 to 1.8 meters (males), 1.4 to 1.6 meters (females)
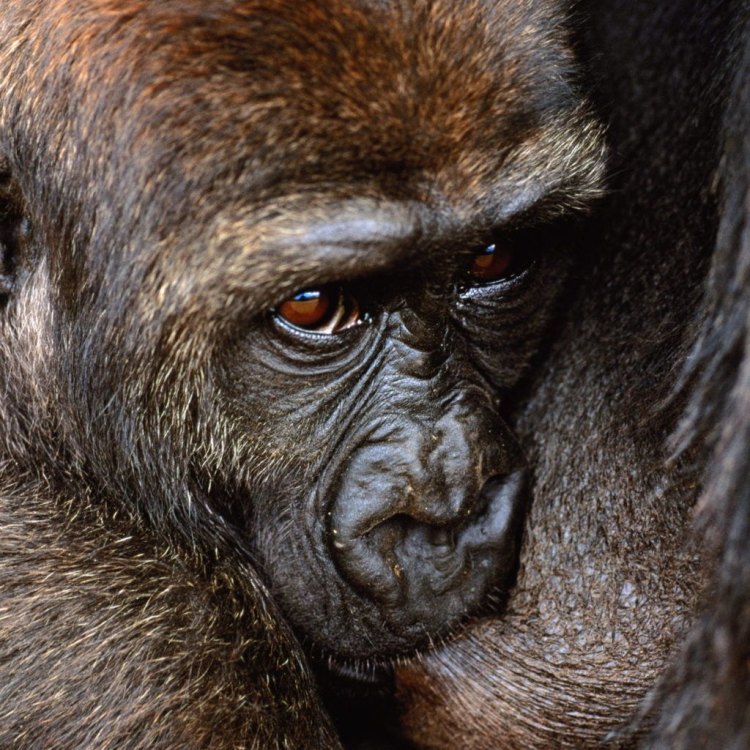

Eastern Gorilla
- Adult Size: 140 to 205 kilograms (males), 68 to 113 kilograms (females)
- Average Lifespan: 35 to 50 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Polygamous
- Sound or Call: Loud roars, hoots, and screams
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Troops
- Behavior: Diurnal and arboreal
- Threats: Habitat loss, poaching, and civil unrest
- Conservation Status: Endangered
- Impact on Ecosystem: Seed dispersers
- Human Use: Tourism
- Distinctive Features: Large size, silver-gray back hair in males
- Interesting Facts: Eastern gorillas are the largest primates on earth
- Predator: No significant natural predators
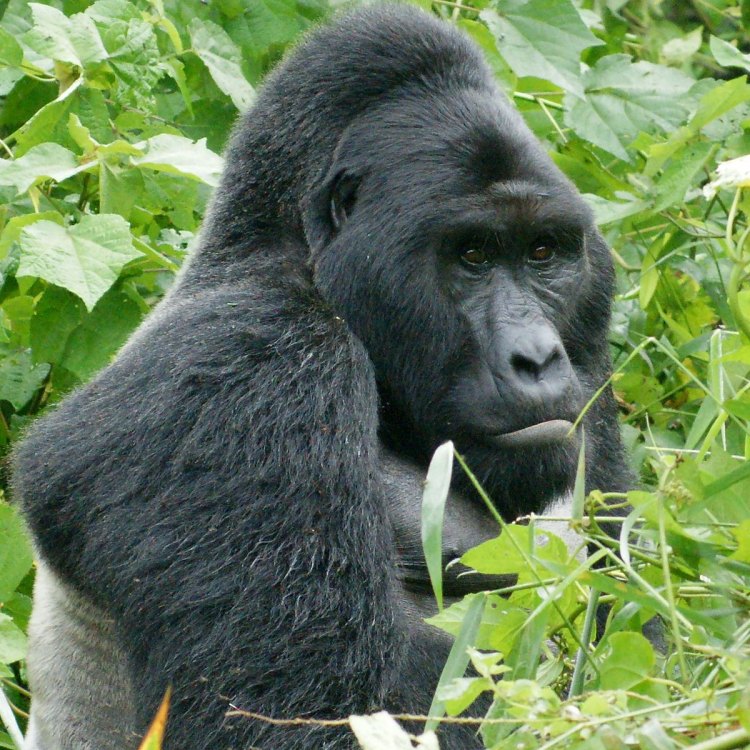

Gorilla beringei
The Mighty and Endangered Eastern Gorilla: A Fascinating Primate of the African Rainforest
Deep in the lush, dense rainforests of Central and Eastern Africa, a mighty and endangered creature roams. The Eastern Gorilla, scientifically known as Gorilla beringei, is one of the most fascinating creatures on our planet. With its impressive size, unique behavior, and critical role in the ecosystem, this primate has captured the attention of scientists, conservationists, and animal lovers alike.The Eastern Gorilla is a species that comprises two subspecies: the Eastern Lowland Gorilla (Gorilla beringei graueri) and the Mountain Gorilla (Gorilla beringei beringei) PeaceOfAnimals.Com. Both subspecies share many similarities, but also have distinct physical and behavioral differences. In this article, we will focus on the Eastern Lowland Gorilla, also known as the Grauer's Gorilla, and explore its unique features, behavior, and role in the ecosystem.
The Physical Characteristics of the Eastern Gorilla
The Eastern Gorilla is the largest living primate on earth, with males reaching an impressive weight of 140 to 205 kilograms, and females ranging from 68 to 113 kilograms. It is also one of the tallest primates, with males standing at an average height of 1.8 to 1.9 meters. These majestic creatures are covered in thick, silver-gray hair, giving them their distinctive appearance.One of the most striking features of the Eastern Gorilla is the large, muscular back in males. This is a result of the "silverback" stage in their life cycle, where males develop a thick strip of silver hair on their back and are considered the dominant member of the troop Eastern Dobsonfly. The silverback also exhibits a larger head and mouth, which is used for loud roars, hoots, and screams that can be heard from miles away.
The Eastern Gorilla has a herbivorous diet, mainly consisting of fruits, leaves, and stems. To accommodate their size and dietary needs, their jaw muscles and teeth are well-developed. This allows them to crush and grind tough vegetation, making them essential seed dispersers in the ecosystem.
Reproduction and Social Behavior
The Eastern Gorilla is a sexually reproducing species, with females reaching sexual maturity at around 10 to 12 years and males at 7 to 8 years of age. Reproductive behavior is polygamous, where one male dominates over a troop of several females. The dominant male also has the privilege of choosing which female to mate with and can have up to three or four mates at a time.The social structure of the Eastern Gorilla is complex and revolves around one dominant male, also known as the silverback. The silverback is responsible for protecting the troop from potential threats, leading them to food sources, and settling disputes within the troop. The other members of the troop include females and their offspring, as well as a few subordinate males. Troops can have up to 30 members, making it the largest social group among primates.
Eastern Gorillas are diurnal and arboreal creatures, meaning they are active during the day and live in trees. They construct nests to sleep in at night, weaving branches and leaves together to create a comfortable bed. Each night, the troop will build a new nest in a different location, making it difficult for predators or other threats to locate and attack them.
Threats to Survival
The Eastern Gorilla faces many threats to its survival, mainly due to human activities. Habitat loss is one of the significant factors affecting this species, with deforestation and land development destroying their natural habitat. This loss of habitat also leads to food scarcity, forcing gorillas to move to new areas in search of food, putting them in conflict with humans and increasing the risk of poaching.Poaching is another significant threat to the Eastern Gorilla. Their body parts, including hands and heads, are used as trophies and sold on the black market. This illegal trade not only contributes to the decline of the species but also funds criminal activities, such as the ongoing civil unrest in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
The Conservation Status of the Eastern Gorilla
Unfortunately, due to these threats, the Eastern Gorilla is currently listed as an endangered species on the IUCN Red List. The population of Grauer's Gorilla, in particular, has significantly declined in recent years, with an estimated remaining population of only 3,800 individuals. Conservation efforts, such as habitat protection and anti-poaching initiatives, are critical to the survival of this magnificent species.The Importance of Eastern Gorillas in the Ecosystem
Eastern Gorillas play a vital role in maintaining the balance of the African rainforest ecosystem. As seed dispersers, they contribute to the regeneration of plant life, and their large size and strength aid in creating openings in the canopy, allowing sunlight and rain to reach the forest floor. This benefits a wide range of species, from insects and birds to other animals that rely on the rainforest for survival.Humans and Eastern Gorillas
Despite the many threats and challenges, humans and Eastern Gorillas have a complex and intertwined relationship. Historically, gorillas have been viewed as fearsome and aggressive creatures, leading to their persecution and exploitation. However, in recent years, there has been a shift towards conservation and ecotourism, with humans working to protect and conserve these magnificent animals.Tourism has emerged as a significant economic factor in Eastern Gorilla range countries, contributing to local economies and fostering job opportunities. Tourist activities, such as gorilla trekking, provide a sustainable and responsible way for humans to interact with gorillas and observe them in their natural habitat. This not only supports conservation efforts but also raises awareness and appreciation for these endangered creatures.
Interesting Facts about Eastern Gorillas
- Eastern Gorillas are the largest primate species on earth, weighing up to 205 kilograms.- They are the only primates that build nests to sleep in at night.
- Eastern Lowland Gorillas can consume up to 40 kilograms of food in a single day.
- Gorillas share 98% of their DNA with humans, making them our closest living relatives.
- They have unique nose prints, just like humans have unique fingerprints.
- Unlike popular belief, gorillas are calm and peaceful creatures, only resorting to violence as a last resort.
The Future of the Eastern Gorilla
The Eastern Gorilla is a symbol of strength, resilience, and the fragility of our natural world. With its large size, impressive social structure, and unique behavior, it continues to fascinate and captivate us. However, time is running out for these magnificent creatures, and urgent actions are needed to ensure their survival.Individuals can contribute to the conservation of Eastern Gorillas by supporting responsible tourism, donating to conservation organizations, and raising awareness about the threats these creatures face. Governments and policymakers must also take swift action to protect the gorilla's habitat, enforce anti-poaching laws, and address the root causes of deforestation and civil unrest.
Thanks to conservation efforts and ecotourism, there is still hope for the Eastern Gorilla to thrive in its natural habitat. Every single one of us has a role to play in ensuring the survival of this iconic species, and it is up to us to take action before it's too late. Let us continue to appreciate, respect, and protect this fascinating primate of the African rainforest for generations to come.
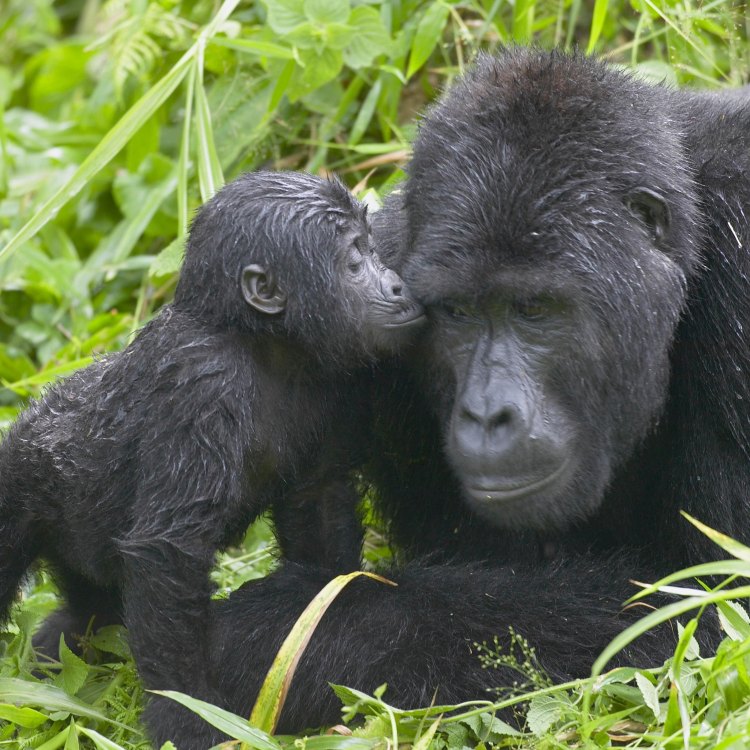

The Magnificent Eastern Gorilla: Exploring the Kingdom of the Largest Living Primate Species
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.